Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is a common condition that affects the tendon responsible for supporting the arch of the foot. When this tendon becomes inflamed, stretched, or torn, it can lead to progressive flattening of the foot and impair overall mobility. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and recovery process for PTTD.
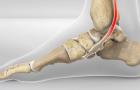
PTTD occurs when the posterior tibial tendon, which runs along the inside of the ankle and foot, fails to function properly. This tendon plays a crucial role in supporting the arch and stabilizing the foot during walking. Dysfunction can lead to flatfoot deformity and increasing pain if left untreated.
PTTD can result from:
PTTD often develops gradually, with symptoms including:
PTTD progresses through four stages:
A healthcare provider can diagnose PTTD through:
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition:
Surgery may be necessary for advanced cases or when conservative treatments fail. Options include:
Recovery from PTTD treatment varies based on the method:
To reduce your risk of PTTD:
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is a progressive condition that can significantly impact mobility and quality of life if left untreated. With timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many individuals can manage symptoms effectively and prevent further progression. If you are experiencing symptoms of PTTD, consult a healthcare provider to explore your options.
For more information on foot and ankle health, explore our blog or schedule a consultation with one of our specialists today.
See why our patients love our physicians, quality of care, and amazing results.
*Based on Independent Market Research


© 2024, North Texas Orthopedics & Spine CENTER. All rights reserved.