A fracture of the heel bone, or calcaneus, is a serious injury that often results from high-impact trauma. As the largest bone in the foot, the calcaneus plays a critical role in weight-bearing and movement. A fracture to this bone can lead to significant pain, swelling, and long-term complications if not treated properly. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and recovery process for calcaneus fractures.
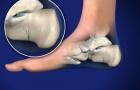
A calcaneus fracture refers to a break in the heel bone, which is located at the back of the foot. This type of fracture often occurs due to high-energy injuries and can significantly impact a person’s ability to walk and bear weight.
Common causes of calcaneus fractures include:
Signs of a calcaneus fracture may include:
A healthcare provider can diagnose a calcaneus fracture through:
Treatment depends on the severity of the fracture and may include:
Non-surgical treatments are generally recommended for minor, non-displaced fractures.
Surgery is often necessary for complex or displaced fractures. Common surgical procedures include:
Recovery times vary but generally include:
Calcaneus fractures can lead to complications, including:
To reduce the risk of a calcaneus fracture:
A calcaneus fracture is a serious injury that requires prompt medical attention and a comprehensive treatment plan. Whether treated conservatively or surgically, proper care and rehabilitation are crucial for ensuring optimal recovery. If you suspect a calcaneus fracture, consult a healthcare professional immediately to begin the appropriate treatment.
For more information on foot and ankle health, explore our blog or schedule a consultation with one of our specialists today.
See why our patients love our physicians, quality of care, and amazing results.
*Based on Independent Market Research


North Texas Orthopedics will be closed on December 25 in observance of the holidays. Wishing you a joyful season!