A fracture of the greater tuberosity is a common shoulder injury. It affects the upper part of the humerus, which is the bone in the upper arm. The greater tuberosity is an important bony bump at the top of the humerus. It is where several key muscles attach, including the rotator cuff.
These muscles are essential for shoulder movement and stability, making a fracture in this area potentially debilitating. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for a fracture of the greater tuberosity.
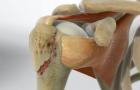
The greater tuberosity is a large, bony prominence located at the top of the humerus. It is the attachment point for muscles important for shoulder movement. This includes the rotator cuff muscles: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. These muscles help control arm motion and stabilize the shoulder joint.
A fracture in this part of the humerus can affect how these muscles work. This can cause pain, weakness, and a limited range of motion in the shoulder.
The most common cause of a greater tuberosity fracture is a traumatic injury, often resulting from falls or accidents. Here are some of the main causes:
A greater tuberosity fracture can present with several noticeable symptoms, which may include:
If you experience any of these symptoms following an injury, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to diagnose and treat the condition.
To diagnose a greater tuberosity fracture, healthcare providers will begin with a physical examination to assess the shoulder’s range of motion and tenderness. They may also perform imaging tests, such as:
Treatment for a greater tuberosity fracture depends on the severity of the injury, the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health. The primary goal is to restore shoulder function and relieve pain.
The recovery time for a greater tuberosity fracture can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the type of treatment required. Non-surgical treatment typically takes a few weeks to a few months for the bone to heal. However, surgery may require a longer recovery period.
Rehabilitation plays a critical role in recovery. A physical therapist will guide the patient through a series of exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles, improve range of motion, and restore function. Full recovery can take a few months. Returning to sports or intense activities may take 4 to 6 months or longer.
While some causes of greater tuberosity fractures, such as falls or accidents, cannot be prevented, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
A fracture of the greater tuberosity can be a painful and disabling injury, but with the right diagnosis and treatment, many individuals can recover fully and regain their shoulder function. Whether treated conservatively with physical therapy or through surgery, proper care and rehabilitation are crucial to recovery. If you think you have a greater tuberosity fracture, see a healthcare professional. They can help you get the right treatment for your condition.
See why our patients love our physicians, quality of care, and amazing results.
*Based on Independent Market Research


© 2024, North Texas Orthopedics & Spine CENTER. All rights reserved.