A scaphoid fracture is one of the most common types of wrist fractures, often occurring after a fall onto an outstretched hand. The scaphoid bone, a small, boat-shaped bone near the base of the thumb, is essential for wrist stability and function. Despite its size, this bone plays a vital role in wrist movement and bearing weight during daily activities. However, its limited blood supply makes it prone to complications if not treated properly. Without prompt care, a scaphoid fracture can lead to chronic wrist pain, arthritis, and loss of motion.
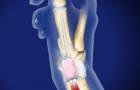
A scaphoid fracture is a break in the scaphoid bone, one of the eight small bones that form the wrist joint. Located on the thumb side of the wrist, the scaphoid connects the two rows of carpal bones, contributing to the flexibility and stability of the wrist. This bone’s unique location and function make it susceptible to injury, particularly during falls or high-impact trauma.
A scaphoid fracture commonly occurs when someone falls onto an outstretched hand with the wrist extended. The force of the fall is absorbed by the palm, placing stress on the scaphoid bone and causing it to break.
Athletes in high-impact sports like snowboarding, skateboarding, and football are at higher risk due to frequent falls or collisions.
High-impact injuries, such as car accidents or crushing injuries to the wrist, can also result in a scaphoid fracture.
One of the key symptoms of a scaphoid fracture is pain and tenderness on the thumb side of the wrist, particularly in the anatomic snuffbox, a small depression at the base of the thumb.
Swelling around the wrist and base of the thumb is common and may be accompanied by bruising.
Patients often experience difficulty moving the wrist, gripping objects, or bearing weight on the affected hand.
A healthcare provider will examine the wrist, checking for tenderness, swelling, and restricted movement.
For nondisplaced fractures, where the bone remains aligned, immobilization is often sufficient. A cast or splint is used to stabilize the wrist and allow the bone to heal. This process can take several weeks to months due to the scaphoid’s limited blood supply.
Displaced fractures or those in areas with poor blood supply often require surgery.
Recovery from a scaphoid fracture varies depending on the severity of the injury and the treatment method. Physical therapy is a crucial part of rehabilitation, helping patients regain strength, range of motion, and functionality in the wrist. Exercises targeting the wrist and hand are essential to restore grip strength and prevent stiffness.
If not treated promptly, a scaphoid fracture can lead to:
A scaphoid fracture is a serious injury that requires prompt diagnosis and proper treatment to ensure full recovery and prevent long-term complications. Without timely care, the fracture may result in chronic pain, arthritis, or reduced wrist function. If you suspect a scaphoid fracture, seek medical attention immediately. With the right treatment and rehabilitation, most patients can regain full wrist strength and function, allowing them to return to their daily activities pain-free.
See why our patients love our physicians, quality of care, and amazing results.
*Based on Independent Market Research


North Texas Orthopedics will be closed on December 25 in observance of the holidays. Wishing you a joyful season!